GeoServer Blog
GeoServer 2.27.5 Release
GeoServer 2.27.5 release is now available with downloads (bin, war, windows), along with docs and extensions.
This is the last scheduled maintenance release of GeoServer series 2.27 - providing existing installations with minor updates and bug fixes. GeoServer 2.27.5 is made in conjunction with GeoTools 33.5, and GeoWebCache 1.27.5.
Are you aware that the all new GeoServer 3 is just around the corner?
And as a special sneak peak, if you’re interested in ARM64 docker images (for example, on AWS, Graviton3 offers a 40% better price performance) then check out this release as a multi-platform (amd64 & arm4) build, which will very soon be merged into the official docker.osgeo.org repo as the new multi-architecture builder going forward.
Thanks to Peter Smythe (AfriGIS) for making this release and driving the ARM64 docker images.
Release notes
Improvement:
- GEOS-12023 Improve developer logging during catalog resources loading and WMS capabilities requests
- GEOS-12033 Allow to configure custom CRS authorities and transformations
- GEOS-12037 Support Metatiling on MapBox Vectortiles
Task:
For the complete list see 2.27.5 release notes.
About GeoServer 2.27 Series
Additional information on GeoServer 2.27 series:
- GeoServer 2.27 User Manual
- CITE Certification achieved
- GeoServer 2025 Q2 Developer Update
- GeoServer 2025 Roadmap
- Content-Security-Policy Headers
- OGCAPI Features Extension
- File system access isolation
- Promote data dir catalog loader to core
Release notes: ( 2.27.5 | 2.27.4 | 2.27.3 | 2.27.2 | 2.27.1 | 2.27.0 )
GeoServer 3 First public release date
We are happy to announce that GeoServer 3 is approaching general availability with a target release date of 15th of April 2026.

This major upgrade modernises the platform’s foundation with the migration to Spring 7 and JDK 17, brings a refreshed user experience and replaces legacy image-processing components with ImageN to deliver significantly improved raster performance and maintainability. The release aligns GeoServer with current Java ecosystems, strengthens security and vulnerability management, and simplifies cloud-native deployments. You can read more about the GeoServer 3 initiative on this page.
GeoServer 3 progress has been made possible by a successful community crowdfunding campaign. This activity is possible due to financial support of sponsors listed below, and a consortium (Camptocamp, GeoCat and GeoSolutions) providing coordination and additional co-funding to move from planning into delivery.
We will publish additional announcements, along with upgrade and testing instructions in the coming weeks. The core team will ask for focused community testing on upgrade paths, high-volume raster workflows,and tiling scenarios. Final QA, packaging and documentation work is ongoing to ensure a smooth upgrade experience and clear operational guidance for administrators.
Watch the usual GeoServer channels for the release announcement and release notes. Contact the project team if your organisation can help with final testing or needs tailored migration assistance.
GeoServer 3 is supported by the following organisations:
Individual donations: Abhijit Gujar, Hennessy Becerra, Ivana Ivanova, John Bryant, Jason Horning, Jose Macchi, Peter Smythe, Sajjadul Islam, Sebastiano Meier, Stefan Overkamp.
GeoServer 2.28.2 Release
GeoServer 2.28.2 release is now available with downloads (bin, war, windows), along with docs and extensions.
This is a stable release of GeoServer recommended for production use. GeoServer 2.28.2 is made in conjunction with GeoTools 34.2, and GeoWebCache 1.28.2.
Thanks to Gabriel Roldan for making this release.
Release notes
Improvement:
- GEOS-11996 Security for STAC/Opensearch for EO
- GEOS-12012 Switching CSVPPIO Strategy from ATTRIBUTES_ONLY_STRATEGY to WKT_STRATEGY
- GEOS-12023 Improve developer logging during catalog resources loading and WMS capabilities requests
- GEOS-12024 Add Git branch name in GEOSERVER_NODE_OPTS
Bug:
- GEOS-10509 WFS Request fails when XML POST body is larger than 8kB
- GEOS-11926 ogcapi plugin makes WFS advertising an outputFormat which is actually unavailable
- GEOS-11979 CloseableIterators not closed by OGC API Features
Sub-task:
For the complete list see 2.28.2 release notes.
Community Updates
Community module development:
- GEOS-11947 Add the ability to skip numberMatched in STAC/OpenSearch for EO responses
- GEOS-12000 Ignore DescribeFeatureType requests without typeName in Features Templating schemas override
- GEOS-12007 Add AWS credential chain authentication UI and documentation for GeoParquet
- GEOS-12013 Support vector datasets ingestion in VectorMosaic via REST
Community modules are shared as source code to encourage collaboration. If a topic being explored is of interest to you, please contact the module developer to offer assistance.
About GeoServer 2.28 Series
Additional information on GeoServer 2.28 series:
CITE 2026 Sponsorship
A major accomplishment in 2025 was re-achieving CITE Certification status for GeoServer. Many thanks to all who were involved! After approximately 10 years, we can once again officially confirm that GeoServer is OGC compliant.
Maintaining Certification is an annual expense for the project - and a sponsorship opportunity for you!
Thanks to Gaia3D and OSGeo:UK for sponsorship covering the expense of CITE Certification for 2025.
Certification January 9th 2026 Deadline
Our 2025 CITE Certification for GeoServer 2.27 expires on January 9th.
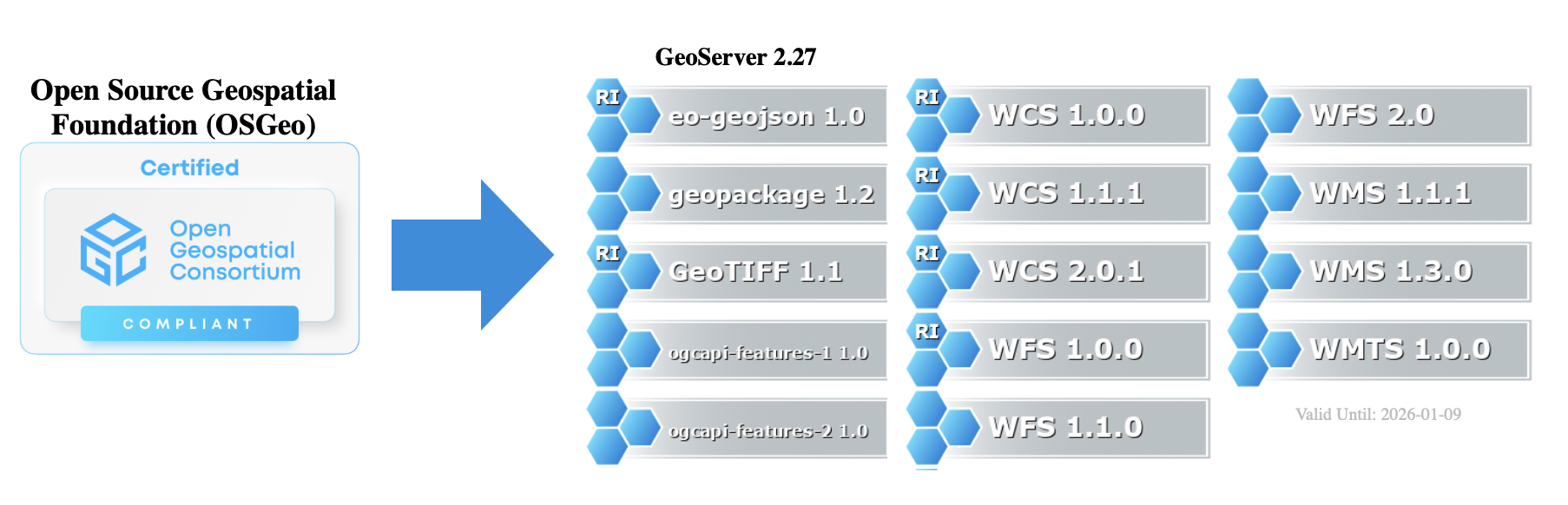
This certification process is an annual expense of around $1000 USD, and we will require sponsorship for 2026 to maintain certified status. GeoServer implements a number of different standards, each one of which costs $150 USD to certify each year. The $150 per certification cost makes use of an agreed on rate offered to the Open Source Geospatial Foundation as a not-for-profit organization. The approximate $1000 USD expense will increase slightly as we gradually adopt additional OGC API standards into the application.
CITE 2026 Sponsorship Opportunity
OGC CITE Certification is important for several reasons:
- Provides assurance that GeoServer may be integrated in solutions as intended by Open Geospatial Consortium.
- Offers an independent source of black-box testing ensuring that each GeoServer release behaves as intended.
- The Provides a logo and visibility for the project helping to promote the use of open standards.
- Inclusion in the list of certified products helps people discover GeoServer, and allows GeoServer to be used by organizations requiring certification.
In addition to CITE certification offering value for the project, sponsoring can provide excellent visibility for potential sponsors, with your logo appearing on the GeoServer home page, and in presentations when each standard is mentioned.


If you/your organization is in position to support this activity, please contact any member of Project Steering Committee, or the OSGeo treasurer. For details visit the GeoServer Sponsorship Page. The more organizations that are able to sponsor, the lower the expense will be to each organization (sharing the approx USD $1,000 per year cost).
Thank you for your support!
CITE 2026 Sponsorship Fulfilled
Sponsorship: Thanks to the following organizations for stepping forward with financial assistance. We are now in position to maintain certification for calendar year 2026.
In-Kind: Thanks to following organizations for “reference implementation” certification. To act as a reference implementation GeoServer must maintain a service operating as an example of how the standard is intended to function. The Open Source Geospatial Foundation has provided hosting, and AfriGIS provided setup and maintenance.
In-Kind: Finally, thanks to the organizations that have directly contributed to passing the test and integrating these tests into our quality assurance workflows.
GeoServer 2.27.4 Release
GeoServer 2.27.4 release is now available with downloads (bin, war, windows), along with docs and extensions.
This is a maintenance release of GeoServer providing existing installations with minor updates and bug fixes. GeoServer 2.27.4 is made in conjunction with GeoTools 33.4, and GeoWebCache 1.27.4.
Thanks to Peter Smythe (AfriGIS) for making this release.
Security Considerations
This release addresses security vulnerabilities and is an important upgrade for production systems.
See project security policy for more information on how security vulnerabilities are managed.
Release notes
Improvement:
- GEOS-12012 Switching CSVPPIO Strategy from ATTRIBUTES_ONLY_STRATEGY to WKT_STRATEGY
Bug:
- GEOS-10509 WFS Request fails when XML POST body is larger than 8kB
- GEOS-11926 ogcapi plugin makes WFS advertising an outputFormat which is actually unavailable
- GEOS-11930 OGC-API extension breaks security REST API
- GEOS-11965 KMZ export incorrectly references remote icon URLs instead of embedding them in the KMZ archive
-
GEOS-11981 POST /security/authproviders 400: Unsupported className - GEOS-11988 Fix bug: preserve metaTilingThreads=0 in saneConfig()
For the complete list see 2.27.4 release notes.
Community Updates
Community module development:
- GEOS-11947 Add the ability to skip numberMatched in STAC/OpenSearch for EO responses
- GEOS-11983 GSR /query fails with HTTP 500 when where parameter is empty
- GEOS-12000 Ignore DescribeFeatureType requests without typeName in Features Templating schemas override
Community modules are shared as source code to encourage collaboration. If a topic being explored is of interest to you, please contact the module developer to offer assistance.
About GeoServer 2.27 Series
Additional information on GeoServer 2.27 series:
- GeoServer 2.27 User Manual
- CITE Certification achieved
- GeoServer 2025 Q2 Developer Update
- GeoServer 2025 Roadmap
- Content-Security-Policy Headers
- OGCAPI Features Extension
- File system access isolation
- Promote data dir catalog loader to core
Release notes: ( 2.27.4 | 2.27.3 | 2.27.2 | 2.27.1 | 2.27.0 )
Behind The Scenes
- GeoServer 3 First public release date
- GeoServer 3 Sprint Update
- GeoServer 2025 Q4 Developer Update
- GeoServer 3 Crowdfunding Goal Surpassed!
- GeoServer 2025 Q2 Developer Update
- GeoServer 3 Crowdfunding – Last Call!
- GeoServer 3 Crowdfunding Campaign Reaches Major Step: 80% Funding Completion
- GeoServer 2025 Roadmap
- GeoServer 2024 Q4 Developer Update
- GeoServer 3 Call for Crowdfunding


































